Standardized cross-sections of reinforced concrete elements
Modern times require the use of standardized shapes and sizes of columns and beams com-posing the load bearing frame of structures. This means regular usage of elements with sec-tions that belong to certain categories. Of course the use of elements with non-standardized sections is not prohibited but it should be made only in certain occasions. When building a structure, the higher the standardization is, the higher the provided quality level and the lower the resulting construction cost.
Standardization serves in:
- the reduction of construction cost since standard moulds and stirrups are more economical,
- the increase of construction quality as usage of standardized formworks and reinforcement helps in maintaining a standard high quality level,
- the familiarization of architects with typical static rules applied to structural members,
- the designers accumulating experience concerning the formation and behavior of construction,
- the faster and problem-free construction and supervision of the structural frame,
- the automatic optimization of the structural frame with the use of PC software.
It is highlighted that the shape and size standardization should not restrict the variety of sections available to the designer. However the latter should make use of it only when it is necessary.
At present there is no official standardization, but based on the regular practices and the typical antiseismic requirements the following format is proposed:
| mm |
250 |
300 |
350 |
400 |
450 |
500 |
600 |
750 |
1000 |
1500 |
2000 |
| 250 |
|
|
|
250x400 |
250x450 |
250x500 |
|
250x750 |
250x1000 |
250x1500 |
250x2000 |
| 300 |
|
300x300 |
|
300x400 |
|
300x500 |
300x600 |
300x750 |
300x1000 |
300x1500 |
300x2000 |
| 350 |
|
|
350x350 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 400 |
|
|
|
400x400 |
|
|
400x600 |
400x750 |
|
|
|
| 450 |
|
|
|
|
450x450 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 500 |
|
|
|
|
|
500x500 |
|
500x750 |
|
|
|
| 600 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
600x600 |
|
|
|
|
| 750 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
750x750 |
|
|
|
- The 450x250 column is highly standardized only as far as the stirrups are concerned, be-cause it is commonly used as integrated column to the ends of both shear walls and com-posite elements.
- When using industrial formworks, it is recommended to avoid usage of 400x400 columns. Moreover, it is preferred to use shear walls with length equal to 1050 mm instead of 1000 mm and 1950 mm or 2100 mm instead of 2000 mm.
| D mm |
300 |
350 |
400 |
450 |
500 |
600 |
750 |
1000 |
| b/d |
250 |
300 |
350 |
400 |
500 |
600 |
750 |
1000 |
1500 |
2000 |
| 250 |
|
|
|
250x450 |
|
|
250x750 |
250x1000 |
250x1500 |
250x2000 |
| 300 |
|
|
|
300x450 |
|
|
300x750 |
300x1000 |
300x1500 |
300x2000 |
According to the specifications issued by the Ministry of Industry, the minimum clear openings in the elevator shaft are:
For common multi-storey residential buildings:
for mechanical movement 1.40 x 1.70 (m)
for hydraulic movement 1.35 x 1.85 ή 1.55 x 1.65 (m)
For buildings with final level floor elevation up to 9.0m:
for 3 persons 1.10 x 1.35 (m)
for 5 persons 1.20 x 1.50 (m)
The opening width of the elevator door must be equal to 1.05 m (rough opening) and the lintel must be placed 2.20 m above the final floor level. This specific width is necessary in order to provide sufficient space to enable a wheelchair user to pass unobstructed through the door even after the jamb has been placed. In multi-storey residential buildings, it is compulsory to construct elevator doors with that width however, its construction is recommended to every oth-er building.
The clear height of the elevator shaft must be at least 3.40 m, calculated from the final level of the upper storey.
The clear depth of the elevator shaft must be at least 1.40 m, calculated from the final level of the first stop.
In order to avoid fatal imperfections especially in the maintenance of the multi-storey structure’s verticality, it is highly recommended to construct the internal space with dimensions at least 50 mm larger than the minimum required. If there are concrete door posts, the elevator door must have a clear opening equal to 1.10 m. Usually elevators have a “Π” shape without door posts, either due to technical reasons or because a sliding elevator door is required. The typical width of the elevator elements (shear walls and door posts) is around 250 or 300 mm.
In all cases, the required dimensions should be verified by the person responsible for the eleva-tor installation.
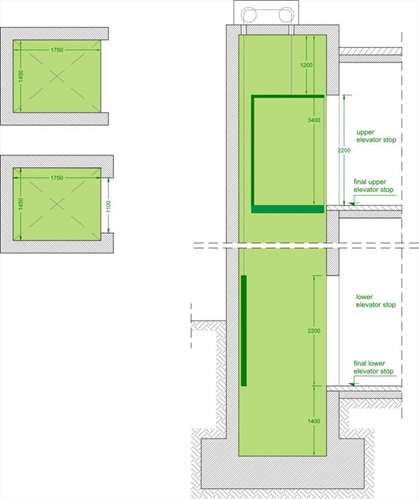 Minimum clear dimensions of an elevator (mm) in a typical multi-storey residential building
Minimum clear dimensions of an elevator (mm) in a typical multi-storey residential building Minimum clear dimensions of an elevator (mm) in a typical multi-storey residential building
| b/d |
250 |
300 |
350 |
400 |
450 |
500 |
600 |
750 |
1000 |
1250 |
1500 |
2000 |
| 20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
|
|
|
250x400 |
|
250x500 |
250x600 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 30 |
|
|
|
300x400 |
|
300x500 |
300x600 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 40 |
|
|
|
|
|
400x500 |
400x600 |
400x750 |
|
|
|
|
| 50 |
|
|
|
|
|
500x500 |
500x600 |
500x750 |
|
|
|
|
- Sections with width lesser or equal than 300 mm, apply to relatively small structures with usual strength requirements.
- When thermal insulation is embedded inside the formwork, the only practical way to standardize this procedure is to use boards with 50 mm thickness since industrial moulds and stirrups usually have dimensions divided by 50.
FOUNDATION CONNECTING BEAMS
| b/d |
350 |
400 |
450 |
500 |
600 |
800 |
1000 |
1200 |
1500 |
| 30 |
|
|
|
|
|
300x800 |
|
|
|
| 40 |
|
|
|
|
|
400x800 |
400x1000 |
400x1250 |
|
| 50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
500x1000 |
400x1250 |
500x1500 |