|
« Multistorey plane frame systems
Comparison of multistorey frame and dual systems »
|
Multistorey plane dual systems In the following multistorey plane frame of project <B_532> the interstorey fluctuation of the apparent stiffness factors kj and the moment distribution factor aj in both columns and wall is presented.  Figure 5.3.2-1: Four-storey dual type structure comprising two columns and a wall
Figure 5.3.2-1: Four-storey dual type structure comprising two columns and a wall Figure 5.3.2-1: Four-storey dual type structure comprising two columns and a wall If the frame also comprises walls, the differences in stiffnesses and in moment distributions become more intense as the number of stories increase. 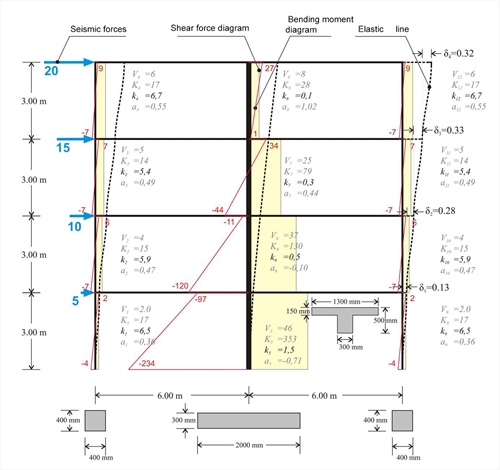 Figure 5.3.2-2: Multistorey dual type structure with triangular distribution of seismic forces( "hand-made" graphical representation)
Figure 5.3.2-2: Multistorey dual type structure with triangular distribution of seismic forces( "hand-made" graphical representation) Figure 5.3.2-2: Multistorey dual type structure with triangular distribution of seismic forces( "hand-made" graphical representation) Example 5.3.2 (3rd storey) : Column stiffnesses: K3,1=4.6/0.329=14, K3,2=25.9/0.329=79 K3,3=4.6/0.329=14. Storey stiffness: Κ 3 = (20+15)/0.329=107. The apparent relative stiffness of the storey can also derive from the sum of its column stiffnesses, i.e. K3= K3,1+K3,2+ K3,3=107. If shear effect is taken into account (Shear effect=ON), the displacements are δ 1 =0.14, δ 2 =0.30, δ 3 =0.34, δ 4 =0.32 mm, i.e. the difference is small. If, however, rigid bodies effect is taken into account (Rigid body=ON), the displacements obtained are significantly smaller equal to δ 1 =0.12, δ 2 =0.22, δ 3 =0.24, δ 4 =0.21 mm, leading to much larger stiffness values. In case of a basement, zero seismic forces are developed at its roof level. However the fixed end condition applies at the bases only of the columns located at the basement perimeter walls.
|
« Multistorey plane frame systems
Comparison of multistorey frame and dual systems »
|

|